Time-tested Ways To Shield Control Cable
페이지 정보
작성자 Columbus 댓글 0건 조회 3회 작성일 24-12-18 02:39본문
 A major supply of radiation from electronic products is due to frequent-mode currents on the external cables. AM and FM radio transmitters can induce high-frequency rf currents into the cable shield. From the attitude of RF interference only, the shield will be left floating. Thus, the shield for the twisted pair can be dedicated for low-frequency shielding solely, and nonetheless offering acceptable EMI/EMC performance. If the bottom aircraft is bonded to the chassis at the best aspect of the board, while the cable enters on the left side of the circuit board, this potential distinction would cause a typical-mode noise current to circulate, degrading the EMI/EMC performance of the system. Connecting the shield at each ends create a floor loop, a small difference of ground potential causes a noise current to circulation from one finish to another. Use a triaxial cable with two layers of shields, one is related at one finish for low-frequency shielding, one other is linked at both ends for RF shielding. Idea: Create a excessive-pass filter to stop low-frequency noise current, reminiscent of mains hum, from flowing on the shield or entering the circuit floor. If terminating the shield at both sides is required for top-frequency shielding, while terminating the shield at one facet is required for low-frequency analog techniques to avoid mains hum.
A major supply of radiation from electronic products is due to frequent-mode currents on the external cables. AM and FM radio transmitters can induce high-frequency rf currents into the cable shield. From the attitude of RF interference only, the shield will be left floating. Thus, the shield for the twisted pair can be dedicated for low-frequency shielding solely, and nonetheless offering acceptable EMI/EMC performance. If the bottom aircraft is bonded to the chassis at the best aspect of the board, while the cable enters on the left side of the circuit board, this potential distinction would cause a typical-mode noise current to circulate, degrading the EMI/EMC performance of the system. Connecting the shield at each ends create a floor loop, a small difference of ground potential causes a noise current to circulation from one finish to another. Use a triaxial cable with two layers of shields, one is related at one finish for low-frequency shielding, one other is linked at both ends for RF shielding. Idea: Create a excessive-pass filter to stop low-frequency noise current, reminiscent of mains hum, from flowing on the shield or entering the circuit floor. If terminating the shield at both sides is required for top-frequency shielding, while terminating the shield at one facet is required for low-frequency analog techniques to avoid mains hum.
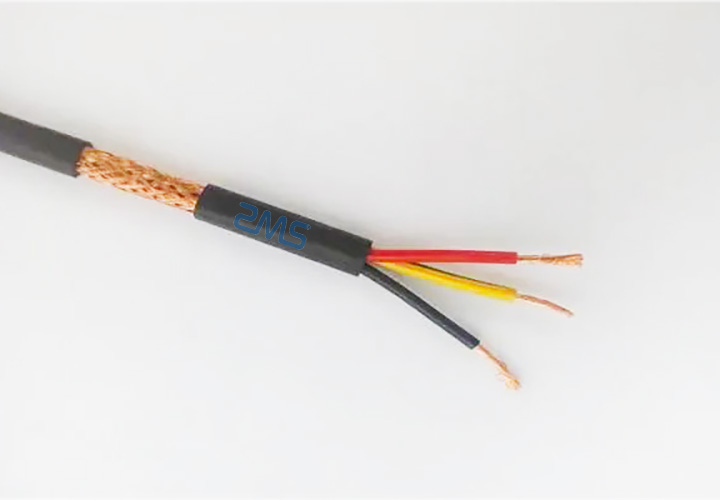 Unfortunately, for low-frequency or analog methods, the low-level noise can cause severe interference. This sacrifices efficient RF shielding, reducing the Faraday cage that is capable of blocking excessive-frequency radiation to a simple electrostatic display screen, solely capable of blocking low-frequency electric fields, like mains hum. The classic drawback is the 50/60 Hz mains hum in audio. The remoted I/O ground plane is the creator's best try to solve this drawback. Connect different non-shield conductors (akin to energy, signal, power ground, sign floor) to the circuit, as ordinary. At this I/O area, a solid connection is made between the chassis and the circuit ground, concurrently, the cable shield is terminated to the chassis at the identical location. The core SCART specification included a primary system of voltage signaling to indicate which device was lively, however in 1998 CENELEC EN 50157-1 was standardized as a versatile serial hyperlink between devices over the SCART cable. For example, much like HDMI, SCART carried bidirectional audio.
Unfortunately, for low-frequency or analog methods, the low-level noise can cause severe interference. This sacrifices efficient RF shielding, reducing the Faraday cage that is capable of blocking excessive-frequency radiation to a simple electrostatic display screen, solely capable of blocking low-frequency electric fields, like mains hum. The classic drawback is the 50/60 Hz mains hum in audio. The remoted I/O ground plane is the creator's best try to solve this drawback. Connect different non-shield conductors (akin to energy, signal, power ground, sign floor) to the circuit, as ordinary. At this I/O area, a solid connection is made between the chassis and the circuit ground, concurrently, the cable shield is terminated to the chassis at the identical location. The core SCART specification included a primary system of voltage signaling to indicate which device was lively, however in 1998 CENELEC EN 50157-1 was standardized as a versatile serial hyperlink between devices over the SCART cable. For example, much like HDMI, SCART carried bidirectional audio.
Coincidentally, this downside also occurs at a much higher scale in industrial installations throughout buildings where a major distinction of "Earth" potential between locations exist. For top-speed RF and digital programs, that is often thought of to be a suitable value - purposeful RF shielding is far more essential than a couple of millivolts of negligible noise, which is below the logic threshold or may be filtered out. For many coaxial and circular connectors, they can be screwed onto the chassis instantly. For instance, a coaxial connector should ideally be screwed onto the chassis instantly, before the same "shield/ground" and center conductor wires attain the circuit board. In an outdated-college design the connectors are screwed onto the chassis, so a shield-to-chassis connection is nearly all the time the prefered path for noise current. But in fashionable designs, connectors are mounted onto the circuit board, not the chassis. Also, be aware that other connections between the chassis and the circuit boards are permitted. But an eventual electrical connection between shield and circuit ground (on account of bonding the circuit ground to the chassis) remains to be permitted.
Only a small bridge is used to connect each planes, allowing excessive-frequency signals to move on high of the bridge without crossing a slot in the airplane, whereas providing a degree of isolation between the circuit floor of chassis gruond. There isn't any way for low-energy data alerts to cross by a transformer, so you want a coupler to provide a knowledge path around the transformer. That is the preferred path of current circulation within the shield. That is an try to resolve the issue of making a shield-to-chassis connection to be the popular path of the RF noise present. Terminating the shield to the chassis, instead of the circuit floor, somewhat mitigates however does not solve the issue of the lack of RF shielding. Unfortunately, actual circuit boards have exterior cables attached, and one of many cable might attach the circuit ground to an external floor, presumably an Earth floor. After the metallic enclosure is zapped by ESD, the circuit floor potential is held by the cable, enabling a secondary ESD strike could develop from the chassis to the circuit ground, lastly leaving the system via an connected cable.
If you cherished this article so you would like to get more info with regards to shield control cable nicely visit our web site.
- 이전글How a Lot does it Cost to be A Bridesmaid? 24.12.18
- 다음글How I Improved My Which Month Was 8 Months Ago In Someday 24.12.18
댓글목록
등록된 댓글이 없습니다.

 치과소개
치과소개 자연치아살리기
자연치아살리기 수면마취
수면마취 임플란트
임플란트 치아교정
치아교정 심미치료
심미치료 일반치료
일반치료 사랑니발치
사랑니발치
 진료철학
진료철학 의료진 소개
의료진 소개 둘러보기
둘러보기 디지털 장비
디지털 장비 소독멸균
소독멸균 리오기공소
리오기공소 무통마취
무통마취 오시는길
오시는길 의료진소개
의료진소개 오시는길
오시는길
 리오가 생각하는 치아
리오가 생각하는 치아 재근관치료
재근관치료 리오가 생각하는 치아
리오가 생각하는 치아 재근관치료
재근관치료
 수면마취란?
수면마취란? 수면 임플란트
수면 임플란트 수면 사랑니발치
수면 사랑니발치 주의사항
주의사항 수면마취란?
수면마취란? 수면임플란트
수면임플란트
 리오가생각하는임플란트
리오가생각하는임플란트 UV임플란트
UV임플란트 전체임플란트
전체임플란트 즉시임플란트
즉시임플란트 비절개 임플란트
비절개 임플란트 네비게이션 임플란트
네비게이션 임플란트 임플란트 틀니
임플란트 틀니 임플란트 재수술
임플란트 재수술 전신질환 임플란트
전신질환 임플란트 임플란트 시술후 관리
임플란트 시술후 관리 리오가생각하는임플란트
리오가생각하는임플란트 UV임플란트
UV임플란트







 심미치료란?
심미치료란? 라미네이트
라미네이트 올세라믹
올세라믹 잇몸성형
잇몸성형 치아미백
치아미백 잇몸미백
잇몸미백 심미치료란?
심미치료란? 라미네이트
라미네이트
 충치치료
충치치료 신경치료
신경치료 치주치료
치주치료 스케일링
스케일링 시린이
시린이 예방치료
예방치료 틀니
틀니 턱관절 치료
턱관절 치료 수면 사랑니발치
수면 사랑니발치 충치치료
충치치료 신경치료
신경치료
 리오가생각하는사랑니발치
리오가생각하는사랑니발치 사랑니발치
사랑니발치 수면사랑니발치
수면사랑니발치 주의사항
주의사항 리오가 생각하는 사랑니발치
리오가 생각하는 사랑니발치 수면사랑니발치
수면사랑니발치