Guide To Gas Patio Heater Regulator: The Intermediate Guide On Gas Pat…
페이지 정보
작성자 Esperanza Neuha… 댓글 0건 조회 10회 작성일 24-10-24 23:30본문
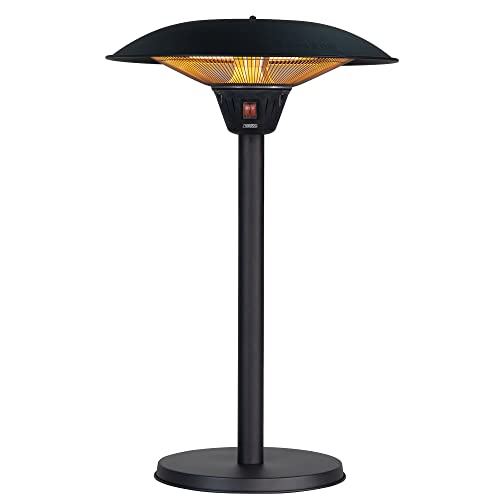
Gas Patio Heater Regulator - Maps.Google.No,
If you're planning on cozying with the cold outside with a propane patio heater, it's important to be aware of how to make use of this device. Matthew Griffith, chief of the prevention department at Montreal's Fire Department, says that shoppers should look for products with safety certifications.
The cheap patio gas heater should be properly connected and there should be no combustible material nearby.
Pressure Regulator
Gas regulators are essentially mechanical appliances that we use in our homes and cars every day without giving them a second thought. Their invention, which took place 135 years ago, has changed the way propane and natural gas are used for cooking, heating and welding with oxy-fuel. There are many variations in the design of regulators however their fundamental function is the same. The regulator is based on an element that senses pressure, usually a fabric-reinforced dialythm to control a valve plug's location and limit the flow of gas.
The diaphragm joins the stem of the valve by rod that runs through the diaphragm and spring before entering the valve. This mechanism detects gas pressure in the home or pipeline and adjusts the valve plug's position to meet the demand. As the consumption of gas in the house decreases and the pressure between the regulator and the house reduces also. The diaphragm is deflated downward and the valve plug is moved closer to the orifice in order to restrict flow. As the demand for gas increases in the home, the valve opens more, thereby increasing the flow.
When the valve plug is closed it is held in position by the spring force until the house's demand decreases, which then opens the valve further to increase the flow. This process, also known as"sizing," is the basic operation of the regulator.
When the valve is opened, a pressure is built up in the main chamber of the regulator, which is connected to the hose outlet port via the venturi tube (see the image). The pressure can be adjusted by turning the handle or screw located on the outside of the regulator. When the screw is turned counterclockwise it increases and decreases the pressure. However, when it is turned clockwise, it decreases the pressure.
When selecting a pressure regulator take into consideration that the nominal maximum and minimum pressure is set by commercial standards and not the pressure of the gas patio heater sale in the supply line. The regulator should be compatible with the hose you are using. Look for a hose labeled whistle-free. It should have alternating rings with different sizes. This will prevent resonant noises from building along the length.
Thermocouple
Thermocouples operate on the premise that different types of metals when in contact at their ends can produce an electric current, even when they are operating at extremely different temperatures. They are used to identify the temperature differences between different points in a circuit and convert that information into an electronic signal that can be read by a thermocouple gauge or other instrument. Thermocouples are superior to other sensors, like thermostors. They can measure extremely high temperatures and operate in harsh environments.
The measuring (or hot) junction is formed by joining two metals that are not compatible at one end, and the other end, the reference (or cold) junction, is maintained at an unchanging temperature. Thermocouples are passive devices which means they do not require power to operate. The voltage produced is proportional to the difference in temperature between the reference and measuring junctions. Thermocouple manufacturers and metrology standard organizations like NIST provide reference tables of the function E (T) Displaystyle scriptstyle e(T) For each specific type of thermocouple.
There are three types of thermocouple connections: exposed grounded and welding. The exposed type of junction extends out of the protective sheath, and provides the fastest response. For measurements in corrosive environments, a grounded thermocouple should be utilized. A welded wire thermocouple is physically insulated from the sheath with mgO powder to stop the penetration of gas or moisture which could cause mistakes.
The thermocouple that is welded also has the added benefit of being more resistant to vibration. It is recommended to use in harsh environments and at pressures of up to 3000 psi. When a thermocouple is damaged, it's usually caused by a lack of polarity. If the sheath does not appear to be properly polarized, the two ends of the thermocouple will have different voltages at the junction of measurement which could result in an inaccurate reading and even cause damage to the instrument. A sensor that is not properly calibrated or installed could also cause a faulty thermocouple.
 Thermostat
Thermostat
Contrary to electric heaters, which need to be wired into the wall gas patio heaters are portable and utilize propane or natural gas cylinders for fuel. The thermostats regulate the flow energy to these cylinders, so they don't spill over, but they still provide heat when required. The thermostat is able to detect the temperature of the air passing through it. The thermostat can also detect whether the room is at a comfortable temperature and shuts off the heating.
Digital thermostats are among the most commonly used. It uses a microcontroller that converts a fluctuating electrical resistance into a measure of temperature. It is able to accomplish this more accurately than older, mercury switch thermostats that used a mercury coil with three wires that would move depending on the temperature. This enabled it to tilt a mercury switch connected to the electrical circuit of a heater or air conditioning unit, turning it on or off.
Another type of thermostat is one that's mechanical. It is a small cylinder filled with wax which begins to melt when it reaches a temperature that is possibly 180 degrees F (different thermostats are open at different temperatures). When the wax is hot, a rod that is connected to the thermostat opens the valve. As the room cools down, the wax contracts and the rod is pulled into the cylinder, closing the valve.
You can set thermostats to change the temperature at various times throughout the day. You can save energy by setting your heating to switch off and on when you're at work or sleeping, instead of having it always on. You can also set your thermostat to come on earlier so that you will arrive home to an appropriate temperature. Thermostats often have a feature called a heat anticipator that prevents the heating system from turning on too early. This is because different parts of the home often reach the set temperature before the thermostat itself.
Pilot Light
Although many modern heating and homes have done away with pilot lights older furnaces and homes still rely on these devices to light the gas in the burner chamber. If the pilot light is ever snuffed out, it's vital to know how to re-light it safely.
A pilot light creates a small flame which heats the thermocouple. The thermocouple produces electricity and keeps the gas fired patio heaters valve open. When the pilot flame ceases to burn the thermocouple cools and ceases to produce electricity, thereby closing the valve. Pilot lights are used on the majority of propane and natural gas appliances, including water heaters.
The process of lighting a pilot light requires first that you shut off the gas valve on the appliance. You will then need to take out any doors or panels that might be blocking access to the pilot light. Find the pilot light tube and carefully follow the instructions on the front of the appliance for opening it. After you've re-lit your pilot light, return the gas valve knob to the "on" position.
 Safety is the main reason for leaving the pilot light on. If it's accidentally turned off the gas constantly venting out of the pilot light tube could build up in your home until a spark from an spark from a cigarette lighter or static electricity ignites it, causing an explosion. To prevent this, pilot tubes are equipped with an integrated cutoff valve.
Safety is the main reason for leaving the pilot light on. If it's accidentally turned off the gas constantly venting out of the pilot light tube could build up in your home until a spark from an spark from a cigarette lighter or static electricity ignites it, causing an explosion. To prevent this, pilot tubes are equipped with an integrated cutoff valve.
In addition to the safety issues, a constantly burning pilot light also consumes an enormous amount of energy. Numerous studies have revealed that a pilot lamp can burn between $7 and $18 of gas each month. This wasted fuel also places a heavier load on the air cooling system in summer. Another concern with a pilot light is that it attracts spiders, which could spin webs that can clog pilot tubes. A flame that is constant can release trace quantities of the compound Mercaptan which is responsible for the smell of rotten eggs that is common in natural gas. If you're concerned about these issues, you should consider purchasing a remote-controlled gas fireplace or replacing your old fireplace with a modern, efficient model.
If you're planning on cozying with the cold outside with a propane patio heater, it's important to be aware of how to make use of this device. Matthew Griffith, chief of the prevention department at Montreal's Fire Department, says that shoppers should look for products with safety certifications.
The cheap patio gas heater should be properly connected and there should be no combustible material nearby.
Pressure Regulator
Gas regulators are essentially mechanical appliances that we use in our homes and cars every day without giving them a second thought. Their invention, which took place 135 years ago, has changed the way propane and natural gas are used for cooking, heating and welding with oxy-fuel. There are many variations in the design of regulators however their fundamental function is the same. The regulator is based on an element that senses pressure, usually a fabric-reinforced dialythm to control a valve plug's location and limit the flow of gas.
The diaphragm joins the stem of the valve by rod that runs through the diaphragm and spring before entering the valve. This mechanism detects gas pressure in the home or pipeline and adjusts the valve plug's position to meet the demand. As the consumption of gas in the house decreases and the pressure between the regulator and the house reduces also. The diaphragm is deflated downward and the valve plug is moved closer to the orifice in order to restrict flow. As the demand for gas increases in the home, the valve opens more, thereby increasing the flow.
When the valve plug is closed it is held in position by the spring force until the house's demand decreases, which then opens the valve further to increase the flow. This process, also known as"sizing," is the basic operation of the regulator.
When the valve is opened, a pressure is built up in the main chamber of the regulator, which is connected to the hose outlet port via the venturi tube (see the image). The pressure can be adjusted by turning the handle or screw located on the outside of the regulator. When the screw is turned counterclockwise it increases and decreases the pressure. However, when it is turned clockwise, it decreases the pressure.
When selecting a pressure regulator take into consideration that the nominal maximum and minimum pressure is set by commercial standards and not the pressure of the gas patio heater sale in the supply line. The regulator should be compatible with the hose you are using. Look for a hose labeled whistle-free. It should have alternating rings with different sizes. This will prevent resonant noises from building along the length.
Thermocouple
Thermocouples operate on the premise that different types of metals when in contact at their ends can produce an electric current, even when they are operating at extremely different temperatures. They are used to identify the temperature differences between different points in a circuit and convert that information into an electronic signal that can be read by a thermocouple gauge or other instrument. Thermocouples are superior to other sensors, like thermostors. They can measure extremely high temperatures and operate in harsh environments.
The measuring (or hot) junction is formed by joining two metals that are not compatible at one end, and the other end, the reference (or cold) junction, is maintained at an unchanging temperature. Thermocouples are passive devices which means they do not require power to operate. The voltage produced is proportional to the difference in temperature between the reference and measuring junctions. Thermocouple manufacturers and metrology standard organizations like NIST provide reference tables of the function E (T) Displaystyle scriptstyle e(T) For each specific type of thermocouple.
There are three types of thermocouple connections: exposed grounded and welding. The exposed type of junction extends out of the protective sheath, and provides the fastest response. For measurements in corrosive environments, a grounded thermocouple should be utilized. A welded wire thermocouple is physically insulated from the sheath with mgO powder to stop the penetration of gas or moisture which could cause mistakes.
The thermocouple that is welded also has the added benefit of being more resistant to vibration. It is recommended to use in harsh environments and at pressures of up to 3000 psi. When a thermocouple is damaged, it's usually caused by a lack of polarity. If the sheath does not appear to be properly polarized, the two ends of the thermocouple will have different voltages at the junction of measurement which could result in an inaccurate reading and even cause damage to the instrument. A sensor that is not properly calibrated or installed could also cause a faulty thermocouple.
 Thermostat
ThermostatContrary to electric heaters, which need to be wired into the wall gas patio heaters are portable and utilize propane or natural gas cylinders for fuel. The thermostats regulate the flow energy to these cylinders, so they don't spill over, but they still provide heat when required. The thermostat is able to detect the temperature of the air passing through it. The thermostat can also detect whether the room is at a comfortable temperature and shuts off the heating.
Digital thermostats are among the most commonly used. It uses a microcontroller that converts a fluctuating electrical resistance into a measure of temperature. It is able to accomplish this more accurately than older, mercury switch thermostats that used a mercury coil with three wires that would move depending on the temperature. This enabled it to tilt a mercury switch connected to the electrical circuit of a heater or air conditioning unit, turning it on or off.
Another type of thermostat is one that's mechanical. It is a small cylinder filled with wax which begins to melt when it reaches a temperature that is possibly 180 degrees F (different thermostats are open at different temperatures). When the wax is hot, a rod that is connected to the thermostat opens the valve. As the room cools down, the wax contracts and the rod is pulled into the cylinder, closing the valve.
You can set thermostats to change the temperature at various times throughout the day. You can save energy by setting your heating to switch off and on when you're at work or sleeping, instead of having it always on. You can also set your thermostat to come on earlier so that you will arrive home to an appropriate temperature. Thermostats often have a feature called a heat anticipator that prevents the heating system from turning on too early. This is because different parts of the home often reach the set temperature before the thermostat itself.
Pilot Light
Although many modern heating and homes have done away with pilot lights older furnaces and homes still rely on these devices to light the gas in the burner chamber. If the pilot light is ever snuffed out, it's vital to know how to re-light it safely.
A pilot light creates a small flame which heats the thermocouple. The thermocouple produces electricity and keeps the gas fired patio heaters valve open. When the pilot flame ceases to burn the thermocouple cools and ceases to produce electricity, thereby closing the valve. Pilot lights are used on the majority of propane and natural gas appliances, including water heaters.
The process of lighting a pilot light requires first that you shut off the gas valve on the appliance. You will then need to take out any doors or panels that might be blocking access to the pilot light. Find the pilot light tube and carefully follow the instructions on the front of the appliance for opening it. After you've re-lit your pilot light, return the gas valve knob to the "on" position.
 Safety is the main reason for leaving the pilot light on. If it's accidentally turned off the gas constantly venting out of the pilot light tube could build up in your home until a spark from an spark from a cigarette lighter or static electricity ignites it, causing an explosion. To prevent this, pilot tubes are equipped with an integrated cutoff valve.
Safety is the main reason for leaving the pilot light on. If it's accidentally turned off the gas constantly venting out of the pilot light tube could build up in your home until a spark from an spark from a cigarette lighter or static electricity ignites it, causing an explosion. To prevent this, pilot tubes are equipped with an integrated cutoff valve.In addition to the safety issues, a constantly burning pilot light also consumes an enormous amount of energy. Numerous studies have revealed that a pilot lamp can burn between $7 and $18 of gas each month. This wasted fuel also places a heavier load on the air cooling system in summer. Another concern with a pilot light is that it attracts spiders, which could spin webs that can clog pilot tubes. A flame that is constant can release trace quantities of the compound Mercaptan which is responsible for the smell of rotten eggs that is common in natural gas. If you're concerned about these issues, you should consider purchasing a remote-controlled gas fireplace or replacing your old fireplace with a modern, efficient model.
댓글목록
등록된 댓글이 없습니다.

 치과소개
치과소개 자연치아살리기
자연치아살리기 수면마취
수면마취 임플란트
임플란트 치아교정
치아교정 심미치료
심미치료 일반치료
일반치료 사랑니발치
사랑니발치
 진료철학
진료철학 의료진 소개
의료진 소개 둘러보기
둘러보기 첨단장비
첨단장비 소독멸균
소독멸균 리오기공소
리오기공소 무통마취
무통마취 오시는길
오시는길 의료진소개
의료진소개 오시는길
오시는길
 리오가 생각하는 치아
리오가 생각하는 치아 재근관치료
재근관치료 엠도게인
엠도게인 리오가 생각하는 치아
리오가 생각하는 치아 엠도게인
엠도게인
 수면마취란?
수면마취란? 수면 임플란트
수면 임플란트 수면 사랑니발치
수면 사랑니발치 주의사항
주의사항 수면마취란?
수면마취란? 수면임플란트
수면임플란트
 리오가생각하는임플란트
리오가생각하는임플란트 UV임플란트
UV임플란트 전체임플란트
전체임플란트 즉시임플란트
즉시임플란트 비절개 임플란트
비절개 임플란트 네비게이션 임플란트
네비게이션 임플란트 임플란트 틀니
임플란트 틀니 임플란트 재수술
임플란트 재수술 전신질환 임플란트
전신질환 임플란트 임플란트 시술후 관리
임플란트 시술후 관리 리오가생각하는임플란트
리오가생각하는임플란트 UV임플란트
UV임플란트







 심미치료란?
심미치료란? 라미네이트
라미네이트 올세라믹
올세라믹 잇몸성형
잇몸성형 치아미백
치아미백 잇몸미백
잇몸미백 심미치료란?
심미치료란? 라미네이트
라미네이트
 충치치료
충치치료 신경치료
신경치료 치주치료
치주치료 스케일링
스케일링 시린이
시린이 예방치료
예방치료 틀니
틀니 턱관절 치료
턱관절 치료 수면 사랑니발치
수면 사랑니발치 충치치료
충치치료 신경치료
신경치료
 리오가생각하는사랑니발치
리오가생각하는사랑니발치 사랑니발치
사랑니발치 수면사랑니발치
수면사랑니발치 주의사항
주의사항 리오가 생각하는 사랑니발치
리오가 생각하는 사랑니발치 수면사랑니발치
수면사랑니발치